EV Battery Technology: Current Trends and Future Prospects

EV battery technology refers to the design, chemistry, & engineering behind the batteries that power electric vehicles. These batteries store and supply the energy needed to run the electric vehicle motor and support other electronic systems.
Nowadays, EV battery technology is advancing rapidly, with efforts to enhance lithium-ion batteries & develop alternatives such as sodium-ion and solid-state batteries. Companies like Suzuki R&D India aim to reduce costs, reliance on raw materials, & improve performance. Key advancements include better cathode materials, optimised battery management systems (BMS), and more efficient recycling and second-life applications, creating sustainable and high-performing solutions for the expanding EV market.
How EV Technology Works?
Electric Vehicles (EVs) do not use petrol or diesel like normal cars. Instead, they run on electricity stored in a battery. Here’s how it works:
- Battery – It stores electricity.
- Electric Motor – Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the wheels.
- Controller –Manages the flow of electricity between the battery & the motor, controlling speed & torque.
- Charging – Allows the vehicle to recharge its battery by plugging into a charging point or regenerative braking, which recovers energy while slowing down.
Benefits of EV Technology
Environmental Benefits
- Reduced Emissions
Electric vehicles (EVs) produce no tailpipe emissions. This helps improve air quality & reduce greenhouse gases. EV Technology is especially important in cities where pollution levels are high.
- Lower Carbon Footprint
Even when considering the electricity used for charging, EVs usually have a smaller carbon footprint compared to petrol or diesel vehicles, making electrification a cleaner mobility solution.
- Less Noise Pollution
EVs are much quieter than traditional vehicles, creating a more peaceful & less noisy environment.
Economic Benefits
- Lower Running Costs
Electricity is generally cheaper than petrol or diesel, which makes EVs more cost-effective to run.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs
With fewer moving parts, EVs require less maintenance, saving both time & money in the long run.
- Incentives & Benefits
Governments provide financial benefits such as tax rebates, subsidies, or discounts on EV purchases.
Other Benefits
- Convenience
EVs can be charged at home or at growing numbers of public charging stations, reducing the need for frequent visits to fuel stations.
- Smooth Driving Experience
EVs provide instant torque, which means faster acceleration, smoother rides, & quieter operation.
- High Performance
Modern EVs are known for their powerful performance & quick response, making them enjoyable to drive.
- Future-Ready
With rapid improvements in battery technology & charging networks, EVs are becoming a smart and sustainable long-term choice.
Electric Vehicle Battery Types
Dominant Technology
- Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used in electric car battery technology today. Their high energy density & lightweight design make them well-suited for modern electric vehicles.
Key advantages:
- High energy storage capacity, allowing a longer driving range
- Lightweight, improving vehicle efficiency
- Long lifespan with low degradation over time
- Fast charging capability
- Essential for daily use
This battery type plays a key role in today’s electric vehicle battery technology. It offers reliable performance & supports features like regenerative braking and smart energy management.
Emerging and Advanced Technologies
1. Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
NiMH batteries are commonly found in hybrid vehicle technology. While they are not as energy-dense as lithium-ion batteries, they offer durability & good thermal performance.
Features:
- Suitable for hybrids that require frequent charging & discharging
- More resistant to temperature fluctuations
- Longer cycle life compared to older battery types
NiMH batteries are less common in full-electric vehicles nowadays. However, they played a key role in early electric vehicle technology & are still reliable in many hybrid models.
2. Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are a major step forward in new electric battery technology. They use solid electrolytes instead of liquid, offering better safety & performance.
Key benefits:
- Higher energy capacity for extended vehicle range
- Faster charging potential compared to traditional lithium-ion
- Improved safety due to reduced risk of leaks or fires
- Compact size, making them suitable for future electric vehicle designs
Solid-state batteries are still in development, but have the potential to transform electric car battery technology. They are well-suited for smart charging systems & modular vehicle designs.
3. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are one of the oldest battery technologies & are rarely used in modern electric vehicles. However, they still serve in low-speed EVs and as auxiliary power sources
Characteristics:
- Low manufacturing cost
- Simple design & widely available recycling systems
They have low energy density & a shorter lifespan, which makes them unsuitable for mainstream electric vehicle battery technology
4. Ultracapacitors
Ultracapacitors aren’t usually the main power source, but they help the electric vehicle motor during acceleration and braking energy recovery.
Benefits include:
- Instant energy discharge and recharge
- Extended battery life when used in combination with traditional batteries
Ultracapacitors are increasingly used alongside batteries in modern EV charging solutions, especially in vehicles that need frequent power boosts or fast charging.
5. Sodium-ion Batteries
Sodium-ion batteries are emerging as an alternative or complement to lithium-ion batteries, using more abundant & cost-effective materials like sodium.
Benefits include:
- Lower cost & reduced reliance on scarce materials
- Sustainable option for large-scale EV production
Sodium-ion batteries are increasingly considered in EV designs, especially where cost & material availability are key concerns.
6. Lithium Titanate (LTO) Batteries
Lithium Titanate batteries are known for their very fast charging, durability, & high safety.
Benefits include:
- Ultra-fast charging & long cycle life
- High safety, even under extreme conditions
LTO batteries are used in EVs where fast charging & durability are critical, though their lower energy density limits widespread adoption.
Key Components of EV Battery
1. Battery Cells
The foundation of every electric vehicle battery type is the cell. Each cell contains an anode, cathode, separator, & electrolyte. Together, they allow the flow of lithium ions during charging and discharging.
2. Battery Pack
Multiple cells form modules, which then make up the battery pack. The pack includes sensors, controllers, & protective casing to ensure safety and efficiency.
3. Cathode
The cathode defines the energy capacity & voltage of the battery. Materials like Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) are widely used in lithium-ion EV batteries.
4. Anode
Typically made of graphite, the anode stores & releases lithium ions. Research is ongoing in silicon-based anodes to further enhance EV battery innovations.
5. Electrolyte
This liquid or gel medium allows ions to move between the cathode & anode. It is essential for smooth charging and discharging cycles.
6. Separator
A thin but critical film that prevents short circuits by keeping the anode & cathode apart, while allowing ion flow.
7. Battery Management System (BMS)
The BMS acts as the brain of the battery. It monitors EV battery efficiency, temperature, voltage, & charging status & ensures safe performance and extends EV battery lifespan.
8. Thermal Management System
Since batteries generate heat, a cooling system maintains optimal temperature. This prevents overheating & improves reliability, especially during fast electric vehicle charging technology.
Making EV Batteries Sustainable: Recycling & Repurposing
As more people buy electric cars, old batteries must be handled carefully. Throwing them away can harm the environment. Automakers are finding ways to recycle & reuse them.
Recycling
Old batteries have useful materials like lithium, nickel, & cobalt. Recycling recovers these materials so they can be used again in new batteries. This reduces waste, pollution, and cost.
Repurposing
Even if a battery is not strong enough for a car, it can still be used. Many old batteries are used for energy storage in homes, offices, & solar or wind plants. This “second life” makes them useful for many more years.
A Greener Future
With EV battery recycling & repurposing, batteries can be reused again and again instead of being thrown away. This makes electric cars cleaner and better for the planet.
What factors determine the performance of a good electric vehicle battery?
The performance of an electric vehicle depends a lot on its battery. A few important factors define how good a battery is:
- Energy Density – This means how much energy the battery can store in a small space. The higher it is, the longer the car can run on one charge.
- Charging Time – Nobody likes waiting too long. A good battery should charge quickly so that the vehicle is ready to use without much delay.
- Battery Life – A battery that lasts longer saves money & also reduces waste, making it better for the environment.
- Safety – Safety is very important. With the help of Battery Management Systems, modern batteries are protected from overheating, short circuits, or overcharging.
- Cost – As technology improves, batteries are becoming cheaper. This helps make electric vehicles more affordable for more people.
The Role of EV Battery Technology in a Sustainable Future
EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, helping reduce urban pollution & dependence on fossil fuels. But it's the electric vehicle battery technology that makes this shift possible.
In fact, batteries in electric cars are getting better every year. Today, most cars use lithium-ion batteries, which are strong & reliable. But scientists are now working on a new type called solid-state batteries. They will be safer & will charge faster, last longer. It will let cars travel farther on one charge. This means less waiting at charging stations & more comfort for drivers.
Another goal is to make batteries affordable. As more are made and new technology improves, the cost will go down. This will make electric cars affordable for more people. With better EV charging technology & more EV charging solutions, the future of electric vehicle technology looks bright.
EVs vs. Conventional Fuels: A Sustainable Shift
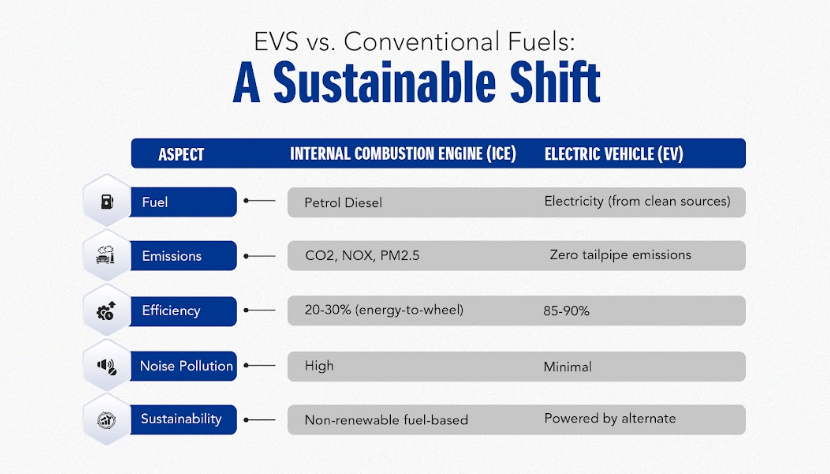
Electric vehicles are 3–4 times more efficient than conventional vehicles & they get cleaner as the power grid gets greener.
Powering a Greener Tomorrow with Suzuki R&D India
As we move toward an electric-first future, electric vehicle battery technology will be the foundation of cleaner, smarter mobility. From the power-packed electric vehicle motor to fast & convenient EV charging solutions, innovation is key. Suzuki R&D India stands committed to developing world-class electric vehicle technology for Indian roads.
